Demystifying Manufacturing Account: A Comprehensive Guide
A manufacturing account is a crucial tool for businesses to track production costs accurately. It provides a detailed breakdown of expenses related to the manufacturing process, helping management make informed decisions. Understanding the intricacies of a manufacturing account is essential for maintaining efficient operations and optimizing profitability. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of a manufacturing account and how it can benefit your business. Let’s explore the key components and importance of this financial tool in detail.
The Importance of Understanding Manufacturing Accounts
Welcome to our blog where we’ll dive into the fascinating world of manufacturing accounts! If you’ve ever wondered how businesses keep track of their production costs, revenues, and profits, then you’re in the right place. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore what manufacturing accounts are, why they are essential for businesses, and how they help in decision-making processes. So, let’s get started!
What is a Manufacturing Account?
Imagine you have a bakery, and every day you bake delicious pastries to sell to your customers. A manufacturing account is like a recipe that helps you keep track of all the ingredients you use, how much they cost, how many pastries you make, and how much revenue you generate from selling them.
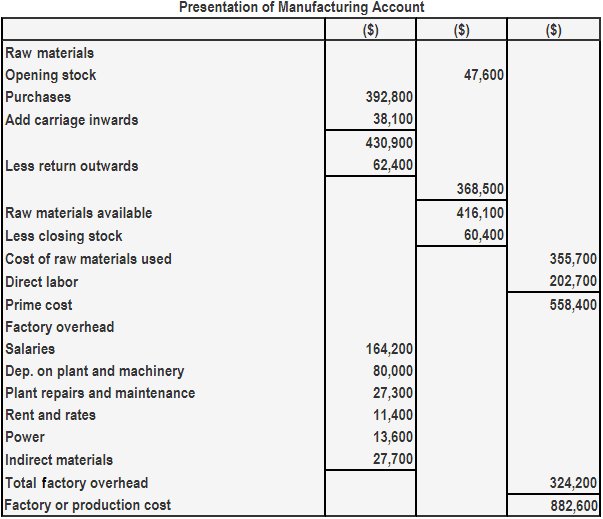
In simple terms, a manufacturing account is a financial statement that shows the costs of production for a specific period, such as a month or a year. It includes direct costs like raw materials and labor, as well as indirect costs like rent and utilities.
Components of a Manufacturing Account
Now, let’s break down the different components of a manufacturing account:
1. Direct Costs
Direct costs are the expenses directly related to the production of goods. This includes the cost of raw materials, labor, and other supplies that go into making the products. For example, in our bakery, the flour, sugar, and eggs would be considered direct costs.
2. Indirect Costs
Indirect costs are overhead expenses that cannot be directly traced to a specific product. These costs include rent, utilities, insurance, and other expenses necessary to run the manufacturing operations. While they are not directly tied to production, they are essential for the business to function.
3. Work in Progress (WIP)
Work in progress refers to the partially completed goods that are still in the production process. In a manufacturing account, the value of WIP is calculated based on the costs incurred up to a certain point in production. This helps businesses track the value of inventory at different stages of completion.
Why Manufacturing Accounts are Important
Now that we understand what a manufacturing account entails, let’s explore why it is crucial for businesses:
1. Cost Control
By maintaining a manufacturing account, businesses can track their production costs and identify areas where they can reduce expenses. This helps in improving efficiency and maximizing profits in the long run.
2. Decision Making
Manufacturing accounts provide valuable insights that help business owners make informed decisions. By analyzing the cost data, companies can determine pricing strategies, assess the profitability of different products, and plan for future investments.
3. Financial Reporting
Manufacturing accounts play a vital role in financial reporting. They provide a detailed breakdown of production costs, which is essential for preparing accurate financial statements and meeting regulatory requirements.
How to Prepare a Manufacturing Account
Now, let’s walk through the steps involved in preparing a manufacturing account:
1. Calculate Direct Costs
Start by calculating the direct costs of production, such as the cost of raw materials and direct labor. This information can usually be obtained from invoices, payroll records, and inventory logs.
2. Determine Indirect Costs
Next, identify and allocate the indirect costs associated with manufacturing, such as rent, utilities, and depreciation. These costs should be distributed among the products based on a reasonable allocation method.
3. Account for Work in Progress
Include the value of work in progress in your manufacturing account to reflect the costs incurred for partially completed goods. This will give you a more accurate picture of the overall production costs.
4. Calculate Cost of Goods Manufactured
Finally, calculate the total cost of goods manufactured by adding up the direct and indirect costs, and adjusting for the change in work in progress inventory. This figure represents the total cost of producing the goods during the period.
In Conclusion
Understanding manufacturing accounts is essential for any business involved in production. By keeping track of production costs, businesses can make informed decisions, control expenses, and improve overall efficiency. We hope this guide has provided you with a clear overview of manufacturing accounts and their significance in the business world. Stay tuned for more insightful articles on financial management and accounting practices!
UNDERSTAND MANUFACTURING ACCOUNTS WITHIN 10 MINUTES!!!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a manufacturing account?
A manufacturing account is a financial statement that shows the costs of production for a manufacturing company. It includes direct materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead costs incurred during the production process.
How is the manufacturing account different from a trading account?
The manufacturing account focuses on the production costs of goods, including raw materials, labor, and overheads, while a trading account only deals with buying and selling finished goods. The manufacturing account is more detailed and specific to manufacturing companies.
What costs are included in the manufacturing account?
The manufacturing account includes direct materials costs (raw materials used in production), direct labor costs (wages of workers directly involved in production), and manufacturing overhead costs (indirect production costs such as utilities, depreciation, and supervision).
How is the manufacturing account useful for a business?
The manufacturing account helps a business track and analyze the costs involved in producing goods. It provides insight into the cost of production per unit, helps in pricing decisions, and enables management to identify areas for cost savings and efficiency improvements.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing account is crucial for businesses to accurately track production costs. By detailing direct materials, direct labor, and overhead expenses, the manufacturing account provides a comprehensive view of manufacturing costs. With this information, companies can make informed decisions to improve efficiency and profitability. Mastering the nuances of the manufacturing account is essential for successful manufacturing operations.